
Call Us
Office Address
Office Hours
Please enter your zip code or city, state below for door-to-door directions.
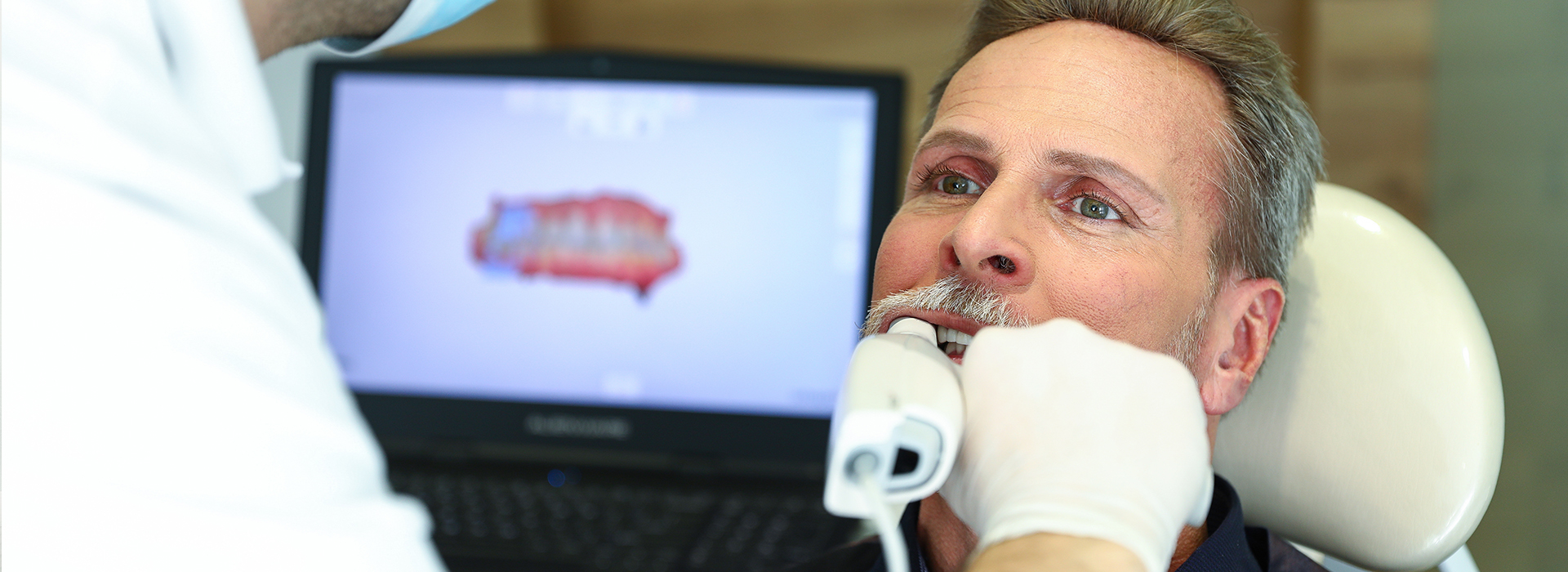
Digital imaging is the modern foundation of diagnostic dentistry: a suite of technologies that create clear, high-resolution views of teeth, gums, and supporting jaw structures. Unlike older film-based X-rays, these systems capture images electronically and display them immediately on a monitor, which helps clinicians assess conditions with far greater clarity. For patients, that means a faster, more informed visit where findings are visible and easier to explain.
These images are not simply sharper pictures; they provide a more complete picture of oral health. Subtle changes in tooth structure, early decay between teeth, and the health of bone around roots are easier to spot. Detecting an issue earlier often leads to less invasive care and more predictable results, because treatment can be planned from a fuller understanding of the area involved.
At our Brooklyn practice, our team uses digital imaging as part of routine exams and as a diagnostic tool for new concerns. The images serve as an objective record that can be reviewed over time to track healing, monitor restorations, and evaluate long-term oral health. This continuity makes follow-up visits more meaningful and supports evidence-based decisions for each patient.
High-resolution digital images let clinicians identify conditions that are not yet causing symptoms, such as tiny cavities, early bone loss from periodontal disease, or minor cracks in teeth. When these problems are caught early, treatment options are generally broader and less invasive. That early-detection advantage is one of the primary reasons digital imaging has become standard in modern dental care.
Digital tools also enhance diagnostic accuracy through image enhancement and manipulation. Clinicians can zoom, adjust contrast, and compare past images side-by-side to spot gradual changes that might otherwise be missed. This capability reduces uncertainty and helps the team choose the most appropriate, targeted approach rather than relying solely on visual inspection or patient-reported symptoms.
Beyond routine care, digital imaging is indispensable when evaluating dental trauma, persistent pain, or unusual oral findings. The speed at which images are obtained and reviewed enables quicker triage and more decisive care planning, which is especially important when early intervention can preserve natural teeth and prevent more complex problems.
Whether you need a crown, an implant, or cosmetic enhancements, treatment outcomes are better when they are planned using precise, up-to-date images. Digital imaging provides accurate measurements of tooth anatomy and jawbone contours, allowing clinicians to design restorations that fit comfortably and function reliably. This level of precision reduces the need for multiple adjustments and helps create results that look and feel natural.
For implant dentistry, integrated digital images are crucial for evaluating bone density, locating important anatomical landmarks, and determining ideal implant positions. Those details inform a surgical plan that prioritizes long-term stability and aesthetic outcomes. The same imaging data is often used to fabricate custom components, improving the fit of crowns and prosthetics and streamlining the restorative process.
In cosmetic dentistry, images help translate aesthetic goals into practical plans. Clinicians can assess tooth proportions and alignment from multiple angles, then communicate recommended changes clearly with patients. When digital records are combined with other advanced tools—like shade-matching and digital smile previews—the result is a predictable pathway to a smile that balances beauty and function.
One of the most tangible benefits of digital imaging for patients is the combination of safety and convenience. Modern sensors capture high-quality images using significantly less radiation than traditional film X-rays, and the immediate availability of images removes the wait time associated with film processing. This speed improves appointment flow and lets clinicians explain findings while the patient is still in the chair.
Because images can be shown and annotated in real time, patients gain a clearer understanding of their oral health. Visual explanations reduce confusion and help people make informed decisions about recommended care. Clinicians can point out areas of concern, demonstrate the intended treatment, and show how different options will affect outcomes—an approach that builds trust and encourages collaboration.
Digital records also support continuity of care. Images are easily archived and retrieved for follow-up visits, referrals, or coordination with specialists. That portability ensures that everyone involved in a patient’s care is looking at the same accurate information, which reduces misunderstandings and improves the efficiency of multi-disciplinary treatment plans.
Digital imaging is often the central hub in a practice that uses multiple advanced tools. When combined with 3D scanning, CAD/CAM design, and guided-surgery software, imaging data creates a seamless workflow from diagnosis to final restoration. These integrations can shorten treatment timelines and raise the predictability of results, because each step is informed by the same precise, digital record.
For example, three-dimensional images can be merged with intraoral scans to produce accurate digital models of a patient’s mouth, which are then used to design crowns, bridges, or implant guides. This digital continuity minimizes manual adjustments and helps produce restorations that align with both functional and aesthetic goals. Ultimately, the patient benefits from fewer appointments and restorations that fit better from the start.
Digital imaging also supports ongoing preventive care by enabling more detailed monitoring between visits. Clinicians can compare sequential images to detect early trends—such as bone changes or the progression of a lesion—and tailor care plans accordingly. In this way, imaging becomes a proactive tool for long-term oral health maintenance rather than a snapshot taken only when problems arise.
At Zhukovsky Dental, we use digital imaging as an essential component of comprehensive, modern dental care. If you have questions about how these technologies will be used during your visit or want to learn more about what digital imaging can reveal for your smile, please contact us for more information.
Digital imaging refers to electronic technologies that capture high-resolution views of teeth, gums, and jaw structures using sensors or digital detectors rather than film. These images display instantly on a monitor, allowing clinicians to review, enhance, and compare results in real time. Because images are produced and stored electronically, they become part of a patient’s clinical record and can be retrieved quickly for follow-up or referral.
The primary purpose of digital imaging is to improve diagnostic clarity and support evidence-based treatment planning. High-quality images reveal subtle changes in tooth structure, early decay between teeth, and bone conditions that may not be evident during a visual exam. Having precise, reproducible images helps the dental team make more informed decisions and explain findings to patients clearly.
Digital imaging enhances diagnostic capability by producing sharper images that can be adjusted for contrast, magnified, and compared side-by-side with prior studies. These manipulation tools make it easier to spot tiny cavities, the beginnings of bone loss, hairline fractures, and other conditions before they progress. Early detection typically allows for less invasive interventions and improved long-term outcomes.
Because images are immediately available, clinicians can correlate radiographic findings with clinical exams during the same visit. This immediacy speeds triage and reduces diagnostic uncertainty, particularly when patients present with vague or intermittent symptoms. Sequential imaging over time also helps the team monitor healing and the stability of restorations or periodontal health.
Modern digital sensors capture images using substantially less radiation than traditional film-based X-rays while maintaining or improving image quality. Equipment is used with protective measures such as lead aprons and thyroid collars when appropriate, and exposures are kept to the minimum required to obtain a diagnostic image. Clinicians follow established guidelines and standards to ensure exposures are justified and optimized for each patient.
For patients with special considerations—such as pregnancy or recent medical imaging—clinicians tailor imaging decisions based on clinical need and timing. Pregnant patients should inform the dental team so appropriate precautions are taken, and elective imaging may be postponed when feasible. Overall, the safety profile of digital imaging combined with current protocols makes it a reliable diagnostic tool.
Digital imaging provides accurate measurements of tooth anatomy and jawbone contours, which are essential for designing crowns, bridges, and implant placements that fit precisely and function well. For implant planning, three-dimensional imaging helps assess bone volume, density, and the location of vital anatomical structures so clinicians can determine optimal implant positions. This level of detail improves surgical predictability and supports the creation of prosthetics that require fewer adjustments.
When combined with CAD/CAM design and guided-surgery workflows, imaging data becomes part of a continuous digital record used from diagnosis through final restoration. Digital files can be transferred to dental laboratories or surgical planning software to fabricate custom components and guides. That continuity shortens treatment timelines and helps produce results that balance long-term function with natural aesthetics.
A digital imaging appointment is typically quick and straightforward: a trained clinician positions the sensor or imaging device, captures the required views, and reviews the images with you on a monitor. Patients remain comfortable during the process and do not experience the chemical processing associated with film X-rays. The clinician may use image adjustments to point out areas of concern and explain recommended next steps while you are still in the chair.
At Zhukovsky Dental in Brooklyn, images taken during routine exams are archived so they can be compared at future visits to track changes over time. If additional views are needed for diagnosis or treatment planning, the team will explain why they are necessary and what information those images will provide. The overall workflow is designed to be efficient and informative for patients.
Digital images become part of a patient’s electronic health record and are stored on secure systems that adhere to professional privacy and security standards. Access to images is restricted to authorized clinical staff and used only for diagnosis, treatment planning, referrals, or patient communication. Practices employ safeguards such as secure servers, encrypted transfers, and access controls to protect health information.
When images are shared with specialists or laboratories, transfers are handled through secure channels and only the necessary data is provided. Patients may request copies of their images for second opinions or personal records, and the practice will provide them in a secure, interoperable format. These processes support continuity of care while maintaining confidentiality.
Yes. Digital imaging reveals conditions beneath the tooth surface and under the gumline that cannot be seen with the naked eye, such as interproximal decay between teeth, root fractures, internal resorption, and early bone loss from periodontal disease. Radiographs and three-dimensional images complement clinical exams by providing an internal view of dental structures and supporting tissues. This complementary information often changes diagnostic impressions and treatment priorities.
Imaging is especially valuable when patients report vague symptoms like intermittent pain or sensitivity, because it helps locate the source of discomfort that may not be apparent on clinical inspection alone. By correlating imaging findings with the oral exam and patient history, clinicians can form a more complete, evidence-based diagnosis and choose targeted interventions.
Digital imaging serves as a central data source that can be merged with intraoral scans and three-dimensional models to create comprehensive digital representations of a patient’s mouth. These combined datasets enable precise CAD/CAM design of crowns, bridges, and surgical guides, and they support guided-implant workflows that translate virtual plans into predictable clinical outcomes. Integration reduces manual steps and improves the fit and function of final restorations.
When imaging and scans are used together, clinicians can simulate restorative or surgical outcomes and refine plans before any physical treatment begins. This preplanning helps minimize chairtime for adjustments and can reduce the number of visits required for complex cases. The result is a more efficient, coordinated process from diagnosis through restoration.
The frequency of updating dental images depends on individual risk factors, clinical findings, and treatment needs rather than a fixed timetable. Patients with active dental disease, ongoing restorative work, recent trauma, or periodontal concerns often require more frequent imaging to monitor progression or healing. Conversely, low-risk patients with stable oral health may need images less often, with decisions guided by clinical exams and professional guidelines.
Clinicians also consider changes in symptoms, new pain, or alterations in oral function when recommending repeat imaging. Because digital images are easy to archive and compare, the practice can tailor imaging schedules to each patient’s history and treatment plan. Open communication about symptoms and routine evaluations helps determine the most appropriate timing for new images.
Digital imaging is an important tool for emergency dental evaluations and the assessment of trauma because it provides rapid, detailed information about fractures, root injuries, tooth displacement, and bone involvement. Quick access to high-resolution images allows the clinical team to triage the situation, identify urgent issues, and develop a timely treatment plan that prioritizes tooth preservation and patient comfort. Imaging guides decisions about whether immediate intervention or specialist referral is necessary.
In trauma cases, sequential imaging is often performed to monitor healing and the success of interventions such as splinting, root canal therapy, or surgical repair. The ability to compare images over time helps clinicians evaluate recovery and detect complications early. This evidence-based approach supports better outcomes for patients after an injury.

Please enter your zip code or city, state below for door-to-door directions.